StrategicRISK survey finds companies likely to be more susceptible to reputation risk
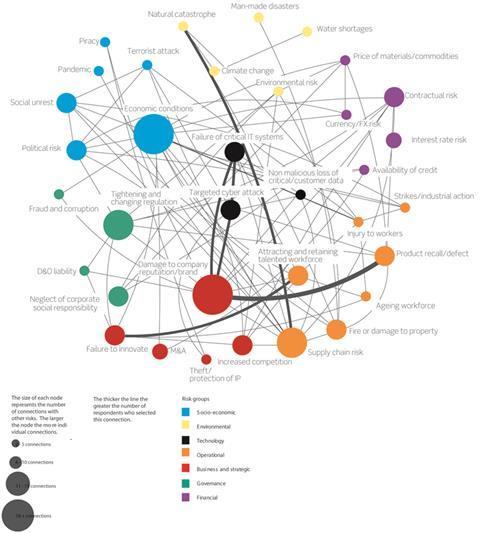
Reputation damage and economic risks are the top two most ‘hyper-connected’ risks, both of which are linked to 20 threats, according to a survey conducted by StrategicRISK.
In October 2015, SR polled 50 risk managers from stock-listed companies across Europe to gain an insight into the interconnected nature of the top 30 risks businesses are dealing with today.
Although reputation damage and economic risks have the same number of connections, businesses may be more susceptible to reputation risk because it is linked to several ‘hyper-connected’ threats (risks with more than 10 connections). For instance, brand damage has strong links to the second and third most hyper-connected threats – targeted cyber-attack (13 links), supply chain disruption (13 links) and tightening and changing regulation (11 links).
But interestingly, more than 20% of respondents said the strongest connection to reputation damage is product recall/defect – a risk often treated as a supply chain issue.
Despite this, risk managers continue to struggle with reputation risk. “It is a big problem because often it is not specifically assessed,” says John Hurrell, chief executive at Airmic. “The conventional way of looking at this is to assume that it is just one of the consequences of a risk on the risk map. As a result, companies are often taken completely by surprise when an occurrence, not previously on the map, has a catastrophic impact on reputation. For example, bid rigging, CO2 emissions manipulation. A specific focus on reputational risk assessment against critical stakeholder dependencies would have identified many of these risks.”
Economic risk, on the other hand, is linked to only one of the top three hyper-connected threats, supply chain disruption.
The majority of respondents said failure to innovate; increased competition; and currency fluctuation are equally the main triggers to economic problems.
Man-made catastrophes and pandemics are the least interconnected risks, with one connection. They have, however, been linked to brand damage and supply chain disruption respectively, both of which have ties to reputation damage.
| Economic conditions | 20 |
| Damage to company reputation/brand | 20 |
| Targeted cyber attack | 13 |
| Supply chain disruption | 13 |
| Tightening and changing regulation | 11 |
| Attracting and retaining talent | 10 |
| Political risk | 9 |
| Failure to innovate | 9 |
| Increased competition | 8 |
| Failure of critical IT systems | 8 |
| Contractual risk | 8 |
| Social unrest | 7 |
| Product defect/recall | 7 |
| Injury to workers | 7 |
| Fire or damage to property | 7 |
| Neglect of social responsibility | 6 |
| Fraud and corruption | 6 |
| Terrorist attack | 5 |
| Strikes/industrial relations | 5 |
| Price of materials/commodities | 5 |
| Non-malicious loss of critical data | 5 |
| M&As | 5 |
| Environmental risk | 5 |
| Natural catastrophes | 4 |
| Currency fluctuation/fx risk | 4 |
| Water shortage | 3 |
| Theft/protection of IP | 3 |
| Piracy | 3 |
| D&O | 3 |
| Climate change | 3 |
| Availability of credit | 3 |
| Ageing workforce | 3 |
| Pandemic | 1 |
| Man-made catastrophes | 1 |



















No comments yet